Breaking the Memory Barrier: Introducing EloqKV on EloqStore
Introduction
The hardware landscape is shifting under our feet. At CES 2026, NVIDIA CEO Jensen Huang delivered a stark warning: the industry is facing a critical shortage of DRAM. While the explosive growth of AI models is the primary driver, there is another massive consumer of memory that often flies under the radar: Caching Services.
From Redis and Valkey to Momento, DragonflyDB, and Garnet, traditional cache services are memory-bound. As data volumes explode, maintaining Terabyte to Petabyte-scale caches in DRAM is becoming prohibitively expensive. The industry needs a new approach—one that delivers the speed of memory with the economics of disk.
Today, we’re proud to introduce EloqKV powered by EloqStore. It is not just another cache; it is a persistent key-value store that speaks the Redis API. It is the first Redis-compatible store designed to deliver consistent, low P9999 latency while harnessing modern NVMe technology to offer up to 20× cost reduction compared to traditional DRAM-based systems.
The Long Tail Problem: Why SSD Caching is Hard
If DRAM is too expensive, the obvious alternative is the SSD. However, for high-performance caching, standard SSD implementations have historically failed. The dealbreaker isn't average latency—it’s long tail latency, especially when dealing with millions or billions of requests per second (RPS).
At the upcoming Unlocked Conference 2026, engineers from Uber will present "Real-world cache lessons from 1B RPS in prod." This highlights the scale modern infrastructure must handle. While a standard PostgreSQL or MySQL setup works fine for low workloads and small hot datasets, it crumbles under the "Internet Scale" traffic processed by Google, Amazon, Uber, and Snap.
The challenge is compounding in the AI Age. We are moving toward a future of Agent-to-Agent communication, which will generate 100x more data and RPS than human interaction. We see this with our own customers: AI chat scenarios involve massive data exploration because prompts are long, complex, and carry context payloads 100x larger than typical human chat messages.
When you throw this level of concurrency at a standard SSD-based database, traditional architectures fail. Relying on multi-threading and synchronous I/O simply cannot guarantee consistent low tail latency (e.g., P9999 < 4ms at 100K RPS) on commodity hardware (like a 16 vCore machine). The threads block, the context switches pile up, and the tail latency spikes.
The Software-Hardware Gap
Our research found that the hardware is no longer the bottleneck. Modern NVMe SSDs are incredibly fast, capable of delivering millions of IOPS (often exceeding 2.5M random read IOPS per drive). The hardware is ready to match the P9999 requirements of a cache. The problem is the software.
To bridge this gap, we had to fundamentally rethink the database engine using two specific techniques:
- Coroutines: To handle massive concurrency without the overhead of OS threads.
- io_uring: The Linux kernel interface that enables high-performance asynchronous I/O.
By combining these, we bypass the limitations of synchronous I/O. You can read more about our engineering philosophy on this topic in our deep dive: Coroutines & Async Programming.
Introducing EloqStore: Open Source & RocksDB-Free
To solve this, we built EloqStore, and we are thrilled to announce that it is now Open Source.
Traditionally, EloqKV utilized RocksDB and RocksCloud as its underlying storage engine. While robust, RocksDB relies on Log-Structured Merge-trees (LSM), which suffer from well-known issues that destabilize long tail latency:
- Write Amplification: Repeatedly rewriting data during compaction.
- Read Amplification: Checking multiple files to find a single key.
- Compression Stalls: CPU spikes during background tasks.
EloqStore addresses these issues head-on by abandoning the traditional Log-Structured Merge-tree (LSM) architecture in favor of a design optimized specifically for the high-parallelism nature of modern NVMe SSDs. While LSM-trees are designed to sequentialize writes for older spinning disks, EloqStore is built from the ground up to exploit the random-access strengths and massive IOPS of modern flash storage.
Deterministic Performance via B-tree Variant Indexing
To achieve deterministic performance, EloqStore utilizes a specialized B-tree variant indexing strategy. It maintains a compact, memory-resident mapping of all non-leaf nodes, ensuring that the internal path to any piece of data is always held in DRAM.
This architecture guarantees exactly one disk access per read. By bypassing the multiple "levels" checks found in RocksDB, EloqStore eliminates the read amplification that typically causes latency spikes during heavy lookups. Whether your dataset is 100GB or 10TB, a read request is always a direct, single-IOPS operation, providing the predictable latency required for mission-critical caching.
High-Throughput Batch Write Optimization
The write path is equally optimized through Batch Write Optimization. Leveraging io_uring, EloqStore bypasses the overhead of traditional synchronous system calls, allowing the engine to group multiple incoming writes into large, aligned blocks. This approach:
-
Reduces the frequency of expensive disk commits.
-
Significantly lowers write amplification.
-
Preserves the lifespan of the SSD while maintaining massive throughput.
Coroutines and Async I/O
Under the hood, EloqStore is built with Coroutines. This allows the system to handle thousands of concurrent requests without the heavy memory footprint or context-switching penalties of OS threads. When an I/O operation is pending, the coroutine simply yields, allowing the CPU to process other requests until the NVMe signals completion via io_uring. This synergy between language-level concurrency and kernel-level asynchronous I/O is what allows EloqKV to maintain sub-millisecond responsiveness under heavy load.
Eliminating the "Compaction Stall"
Most importantly, this architecture eliminates the jitter caused by background maintenance. Traditional LSM-trees must periodically merge and rewrite files to maintain performance—a process that consumes massive CPU and I/O resources, leading to the dreaded "compaction stall." EloqStore’s append-only design manages data reclamation more gracefully, ensuring that background tasks never interfere with foreground traffic. The result is a P9999 latency profile that stays flat, delivering a "memory-like" experience at disk-based economics.
Benchmark: 20x Cost Reduction
We put EloqKV on EloqStore to the test using memtier_benchmark.
The Setup:
- Hardware: Single Node, GCP Z3-16 instance.
- Specs: 16 vCore, 128GB RAM, 2.9TB NVMe SSD * 2.
- Data: Loaded 2TB of data (800 Million items, with large payloads of 1-4KB per item).
The Result: With a load of 100,000 QPS, EloqKV maintained a P9999 latency of under 4ms among different kinds of workloads.
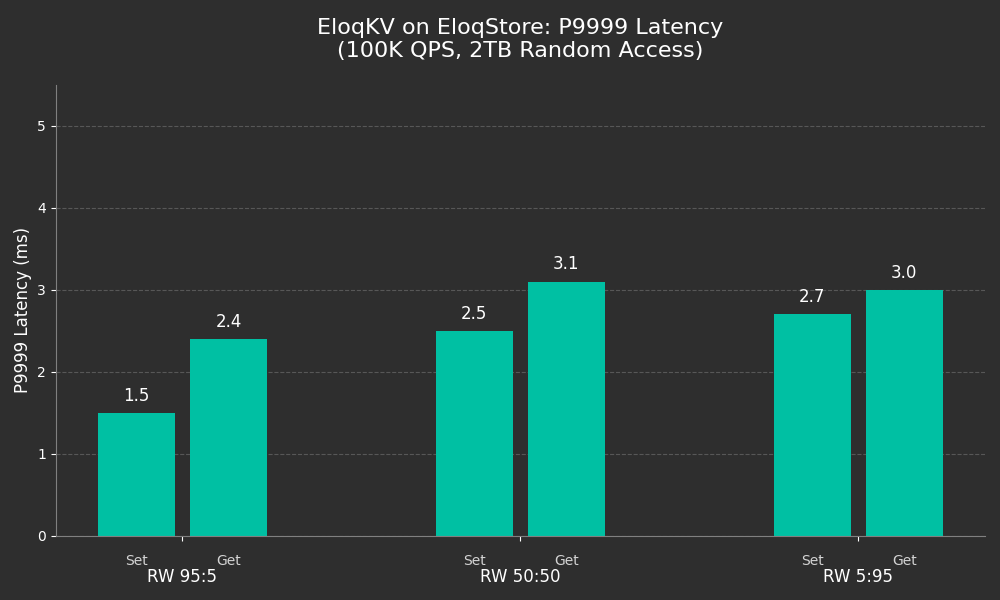
The Comparison: To store this same 2TB dataset in Redis, you would typically require 20 nodes of similar RAM capacity. By leveraging the NVMe SSD with EloqStore, we achieved a 20x cost reduction while keeping the long tail latency low enough to meet strict business requirements.
Rethinking the Key-Value Store for the AI Era
Beyond its performance as a cache, EloqKV is a full-featured key-value store. It does not require you to hold all keys in memory just to maintain performance. This architectural shift enables a new class of advanced features:
-
Cloud-Native "Scale to Zero": Because data is persisted on NVMe and/or object storage rather than volatile DRAM, EloqKV can spin down to zero when idle.
-
AI-Native "Quick Branching": For complex AI workflows and agent simulations, EloqKV supports rapid branching. You can fork your state to explore different prompt chains or agentic outcomes without duplicating massive DRAM footprints.
Meet us at Unlocked 2026
We are excited to announce that EloqData is a sponsor of the Unlocked Conference 2026, hosted by Momento and AWS.
Unlocked is the premier event for developers discussing the future of backend infrastructure. We are eager to discuss how the shift from DRAM to NVMe can unlock new possibilities for AI and hyperscale applications.
Come visit our booth, chat with our engineers, and see EloqStore in action. We look forward to seeing you there
